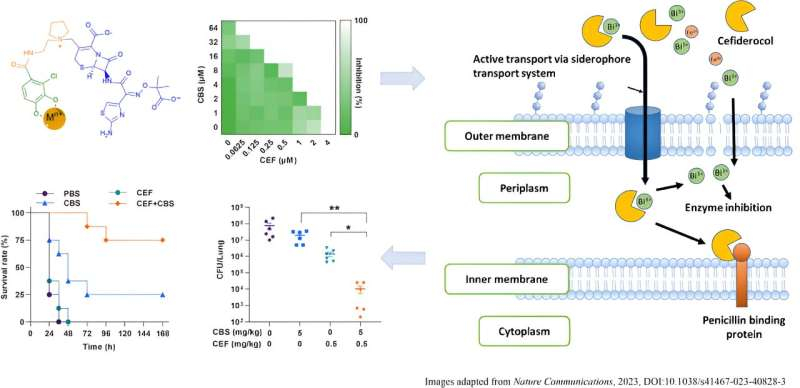
 Figure 1. Bismuth and cefiderocol showed synergistic effect both in vitro and in vivo (lung infectious model) against PAO1, a strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, as a metallo-sideromycin complex transported actively into bacterial cells.
Figure 1. Bismuth and cefiderocol showed synergistic effect both in vitro and in vivo (lung infectious model) against PAO1, a strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, as a metallo-sideromycin complex transported actively into bacterial cells.
In the relentless fight against antibiotic-resistant superbugs, scientists are continuously discovering innovative approaches to target their vulnerability. Like other bacteria, Superbugs have a distinct weakness: their reliance on iron for their growth and survival. Iron is a necessary nutrient for bacteria, supporting important cellular processes such as DNA replication, energy production, and other vital functions. Essentially, iron serves as a 'food' source for bacteria.
Professor Hongzhe SUN and his research team from the Department of Chemistry have devised a strategy called the "Dual Trojan Horse", where a metal-based-drug and sideromycins, a class of antibiotic structurally resembling iron, work together to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria. By leveraging a pathway that mimics iron uptake, these antibiotics can be effectively delivered into bacterial cells. When exposed to sideromycins, bacteria are tricked into believing they are acquiring iron, which leads them to transport these compounds into their cells. This strategy enhances the potency of sideromycins and extends their lifespan, representing a significant breakthrough in the ongoing battle against antibiotic resistance.
These promising results were successfully replicated in a live mice model, introducing an innovative strategy to combat antimicrobial resistance, and offering hope in the fight against superbugs in the clinic. These findings have recently been published in Nature Communications titled "Metallo-sideromycin as a dual functional complex for combating antimicrobial resistance."
"We are short of new antibiotics, and infection caused by resistant bacteria (i.e., superbugs) may lead to another pandemic. We have uncovered a dual Trojan Horse strategy to restore antibiotics activity, such as cefiderocol, and hope to provide a novel arsenal for combating antimicrobial resistance," commented Professor Sun.
The encouraging findings from this study were successfully reproduced in a live mice model, presenting a groundbreaking approach in the fight against antimicrobial resistance and instilling optimism for combating superbugs in clinical settings. These significant findings have recently been published in Nature Communications under the title "Metallo-sideromycin as a dual functional complex for combating antimicrobial resistance."
Link of the journal paper can be accessed from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-40828-3
