
PROFESSOR K.Y. CHAN
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
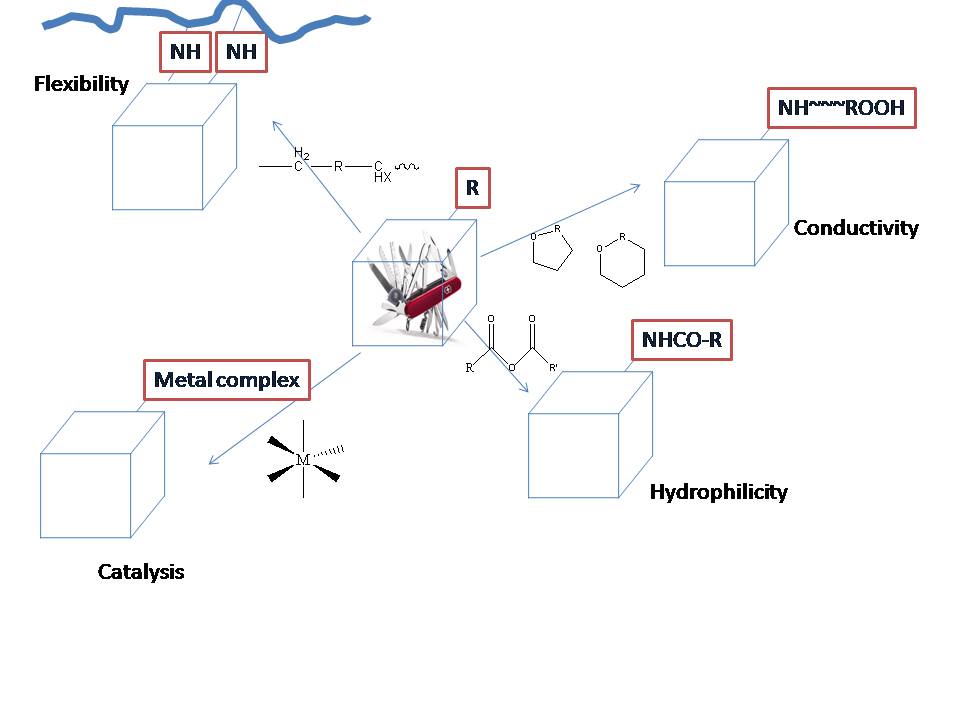
Functionalization of MOFs Towards Multiple Applications
Metal Organic Framework (MOFs) are a new class of very robust materials which are popular for possessing pores of around 2 nm and less. They stand out from other porous materials because of their crystalline properties, together with reasonavle chemical and thermal stabilities; thereby, bridging the gap between organic and inorganic materials. For this reason, they have been used in various processes such as gas capture, storage and separations. Other applications include catalysis, organic and inorganic wastes removal, and even as sacrificial material for nanoparticle syntheses.
MOFs are one of the best materials for selective adsorption of carbon dioxide and hydrogen. Its permanent pore system and corresponding high surface area of MOFs are capable of situating and dispersing metal nanoparticles, which can potentially catalyze the carbon dioxide hydrogenation. Our objective is to convert carbon dioxide to value-added chemicals by taking advantage of MOFs as carbon dioxide capture materials and nanoparticle hosts.
Furthermore, the cavities of MOFs have been very useful in the storage of small molecules, but they may also be useful for hosting macromolecules. Therefore, it is also of interest to explore the synergy of MOFs with polymers for ion-exchange applications.
 |
 |
Proposed applications and targets achievable using MOFs
|
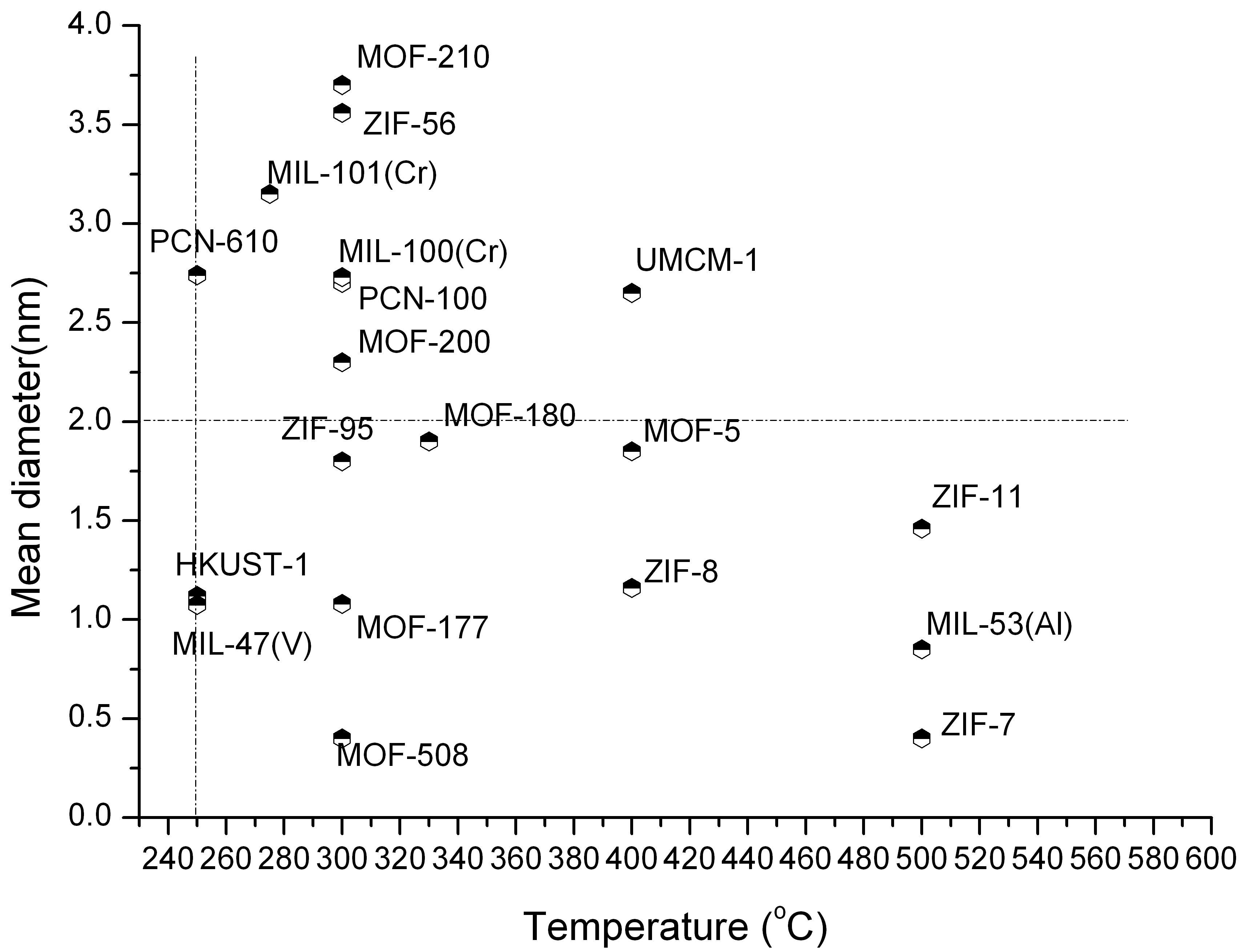
Screening
window for promising MOFs as catalysts with pore size (y-axis) & thermal
stability (x-axis) considerations |
Posters presented in conferences on this work
(Click on image to download pdf version)